In the new Top Cable Low Voltage and Medium Voltage Catalogue, you will find all…
Low voltage electrical cable’s designations (0.6 / 1 KV)
Each low voltage cable has a designation according to the norm. This denomination is composed by a set of letters and numbers, each with a specific meaning. This designation refers to a series of product characteristics (materials, nominal voltages, etc.) that facilitate the most suitable cable selection for your needs, avoiding possible errors in the cable supply.

When a cable does not indicate this data clearly, it may be a faulty cable, which does not meet the safety standards or its proper functioning.
INDUSTRIAL POWER LOW VOLTAGE CABLES 0.6 / 1KV
Industrial power cables 0.6 / 1kV are for industrial power applications in various fields (general industry, public facilities, infrastructures, etc.), and international standards: UNE, IEC, BS, UL.
Some low voltage power examples cables 0.6 / 1kv are the following:
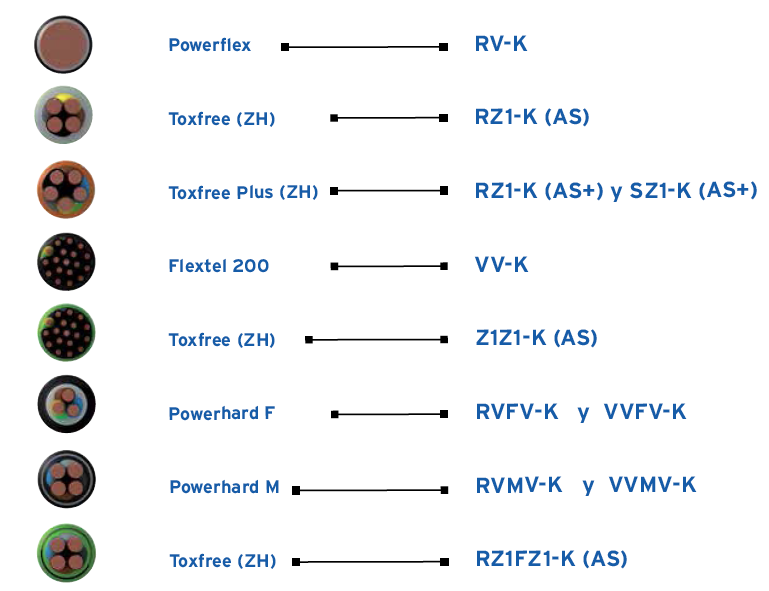
- THE ACRONYM MEANINGS FOR THE COMMERCIAL CABLE’S NAME
What does it mean, for example, RZ1-K on a Top Cable Toxfree ZH RZ1-K cable?

After the manufacturer name (in this case, Top Cable) and the Trademark (Toxfree), the letters and numbers refer to the coatings of the cable, the conductor class, to the nominal voltage and to the composition end of the cable.
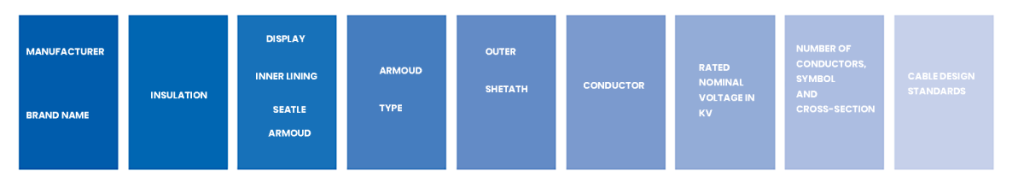
- R is the insulation type, in both cases, is reticulated Polyethylene (XLPE).
- Z1 indicates that this cable has a polyolefin cover not flammable, halogen-free and with low smoke emission and corrosive gases in case of fire. Its designation is Z1.
- K the letter K indicates that it is a flexible copper conductor (class 5), for fixed installations.
- 0.6 / 1 kV indicates that it is a 1000-volt cable (low voltage)
Another example of the acronym’s meaning can be found with the Top Cable Powerhard RMV cable 0,6 / 1kV 3×2,5 UNE 21123 IEC 60502 CE 1201416; which is the following:
- Top cable: Manufacturer
- POWERHARD: Trade name
- RVMV: Cable insulated with PLXLPE (R), with OVC (V) seat, armoured with steel wire core (M) and covered with PVC (V)
- 0,6 / 1kV: The nominal voltage of the cable is 1000V (low voltage)
- 3×2,5: Three-wire cable 2.5 mm2 without am-green
- UNE 21123 IEC 60502: Cable design standards. These standards define exactly what the cable looks like. Thicknesses, material qualities, tests to be carried out, etc. UNE 21123 is the Spanish design standard. IEC 60502 is the standard on which UNE 21123 is based
- CE: CE marking obligatory for the marketing of the product in the European Community. This marking can be on the product or on the packaging
- 090102: Date of manufacture for traceability
LOW VOLTAGE CABLE DENOMINATION 0.6 / 1kV
Each cable has a standard designation. This designation is composed of a set of letters and numbers, each with a specific meaning. This designation refers to a series of product characteristics (materials, nominal tensions, etc.) that facilitate the selection of the most suitable cable for your needs, avoiding possible errors in the supply of one cable by another.
When a cable does not clearly indicate these data, it may be a defective cable, which does not comply with safety regulations or guarantee the cable’s life and proper operation.
The meaning of each letter within each section is as follows:
Designation according to type of insulation
| Nomenclature | Cable type |
|---|---|
| R | Crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE) |
| X | Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) |
| Z1 | Halogen-free thermoplastic polyolefin |
| Z | Halogen-free thermosetting elastomer |
| V | Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) |
| S | Halogen-free thermosetting silicone compound |
| D | Ethylene-propylene elastomer (EPR) |
Screen designation, interior lining, armature seat
| Nomenclature | Cable type |
|---|---|
| C3 | Copper wire screen, helically arranged |
| C4 | Copper shield in the form of a braid, on the assembled insulated conductors. |
| V | Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) |
| Z1 | Halogen-free thermoplastic polyolefin |
If there is no screen, no inner lining and no armature seat, no letter is used.
Designation of the different types of armor
| Nomenclature | Cable type |
|---|---|
| F | Steel strapping arranged in a helical pattern. |
| FA | Aluminium strapping arranged in a helical pattern |
| FA3 | Longitudinally corrugated aluminium strip |
| M | Steel wire crown |
| MA | Aluminium wire crown |
Designation of the outer sheath
| Nomenclature | Cable type |
|---|---|
| V | Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) |
| Z1 | Halogen-free thermoplastic polyolefin |
| Z | Halogen-free thermosetting elastomer |
| N | Vulcanized chlorinated polymer |
Conductor’s designation
| Nomenclature | Cable type |
|---|---|
| K | Flexible copper (class 5) for fixed installations |
| F | Flexible copper (class 5) for mobile services |
| D | Flexible for welding machine cables. When there are no letters on it, the conductor is made of solid copper, class 1 or 2. |
| AL | AL If the conductor is made of aluminium, (AL) is indicated. |
Rated voltage
| Rated | voltage |
|---|---|
| 0,6/1 kV | Rated voltage 1,000V (low voltage) |
Explanation of the number of conductors
| Nomenclature | Cable type |
|---|---|
| nGS | Number and cross-section of wires, in mm2 , with Yellow/Green conductor |
| nxS | Number and cross-section of conductors, in mm2 , without conductor Yellow/Green |
Cable design rules
The cable design rules are also referenced in the marking of each cable:
- UNE 21123
- IEC 60502
- UNE 21150
Additional data
| Nomenclature | Cable type |
|---|---|
| CE | CE CE marking is compulsory for the marketing of the product in the European Community. This marking can be on the product or on the packaging. |
| Manufacture date | Date of manufacture (YYMMDD). The date of manufacture is usually placed for traceability purposes. Traceability makes it possible to know who, when and where has carried out each stage of the process and with which materials. |
You can review concepts through this video that we have prepared:




