Carrying out outdoor electrical installations means taking into account a series of parameters that do…
Electrical Cable Types, Sizes, and Installation
The differents electrical cable types has the purpose of transporting electrical energy from one point to another. Depending on their final application, cables can have different configurations, always basing their design on national and international regulations.

ELECTRICAL CABLE VOLTAGE
An electric cable is measured in volts and, depending on these, they are categorized into one group or another:
- Low voltage cables (up to 750 V): in a variety of applications, and with thermoplastic and thermoset coatings. They are designed and built according to harmonized standards.
- Low Voltage cables (up to 1,000 V): (also called (0,6/1 kV) The cables in this section are used for industrial power installations in various fields (general industry, public installations, infrastructures, etc.). They are designed according to international standards (UNE, IEC, BS, UL).
- Medium Voltage cables: from 1 kV to 36 kV. They are used to distribute electricity from electrical substations to transformer stations.
- High Voltage cables: from 36 kV. They are used to transport electricity from the generating plants to the electrical substations.

TYPES OF ELECTRICAL CABLES BY THEIR USE
Low voltage cables
Cables for electric panels
Flexible cables for wiring electric cabinets. These electric cables are especially suitable for domestic use, for installation in public places and for internal wiring of electrical cabinets, switch boxes and small electrical appliances.
Power cables
Energy cables for industrial facilities and public places. It is common to find power cables in applications for power transmission in all types of low voltage connections, for industrial use and for variable frequency drive (VFD).
Armoured cables
Cables with aluminium or steel reinforcement for installations with risk of mechanical aggression. It is also common to find armoured cables in places where rodents are present, as well as in installations in premises with a risk of fire and explosion (ATEX).
Rubber cables
The use of extra flexible rubber cables is very varied. We can find rubber cables in fixed industrial installations as well as in mobile service. Welding cables should have a rubber sheath, which allows high currents to be transmitted between the welding generator and the electrode.

Halogen-free cables
High Security Halogen Free (LSZH) Cables with low smoke and corrosive gas emission in case of fire are suitable for use in wiring of electrical panels and public places, installations of all kinds in public places, individual derivations, emergency circuits, public distribution networks and also for mobile service.
Fire resistant cables
These cables are specially designed to transmit electrical energy in the extreme conditions that occur during a prolonged fire, guaranteeing supply to emergency equipment such as signalling, smoke extractors, acoustic alarms, water pumps, etc. Their use is recommended in emergency circuits in places with public concurrence.
Control cables
Control cables for fixed or mobile installations should be extremely flexible, as they are mainly designed for small household appliances, for the interconnection of machine parts used for manufacturing, for signalling and control systems, for the connection of motors or frequency converters, for signal transmission where the voltage induced by an external electromagnetic field may affect the transmitted signal or for power supply connections to avoid generating electromagnetic fields.
Instrumentation cables
These are flexible and shielded cables for the transmission of signals between equipment in industrial installations. Especially suitable for optimum data transmission in environments with a high level of electromagnetic interference.
Solar cables
These cables are particularly suitable for connecting photovoltaic panels, and from the panels to the DC to AC inverter. Thanks to the design of their materials and their cover, which is especially resistant to solar radiation and extreme temperatures, they can be installed outdoors with full guarantees.

Special cables
There is a wide variety of electric cables for special installations such as: temporary light garland installations at trade fairs; connections for overhead cranes, hoists and lifts; applications in submerged pumps and drinking water areas such as aquariums, purification systems, drinking water fountains or in swimming pools for lighting, purification and cleaning systems.
Aluminium cables
Aluminium cables for power transmission are suitable for fixed installation indoors, outdoors and/or underground.

Medium Voltage Cables
RHZ1 cables
Medium Voltage Cable type RHZ1 with XLPE insulation, halogen free and non flame and/or fire propagating. They are cables perfectly adapted for the transportation and distribution of energy in Medium Voltage networks.
HEPRZ1 cables
Medium Voltage cable with HEPR insulation, halogen-free and not flame- and/or fire-propagating Ideal for the transportation and distribution of energy in Medium Voltage networks.
MV-90
Medium Voltage cable with XLPE insulation, according to American standard. For transportation and distribution of energy in Medium Voltage networks.
RHVhMVh cables
Copper and aluminium medium voltage cable for special applications. Especially recommended for installations where there is a risk of presence of oils and chemical agents of the hydrocarbon type or their derivatives.

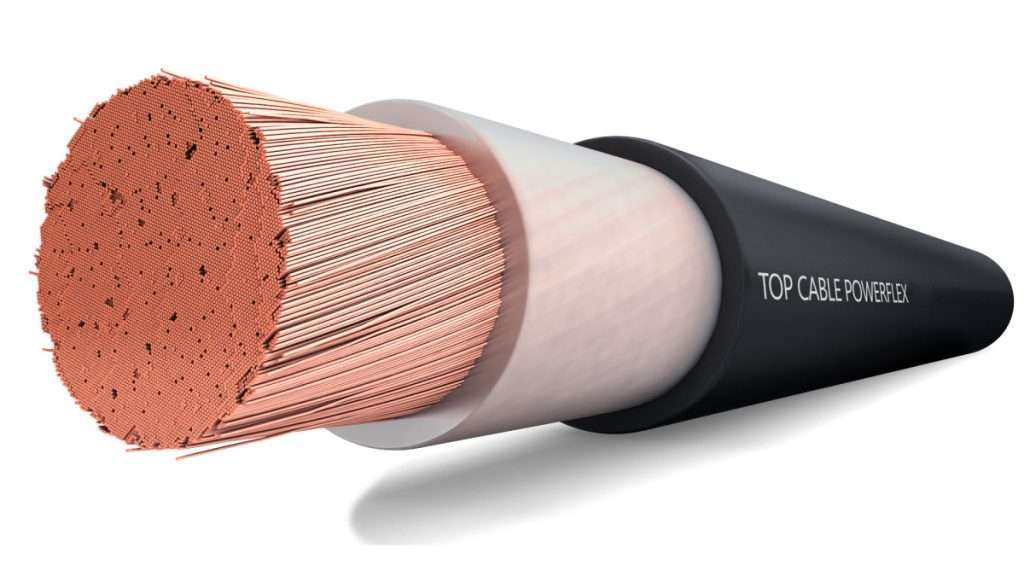
COMPONENTS OF AN ELECTRICAL CABLE
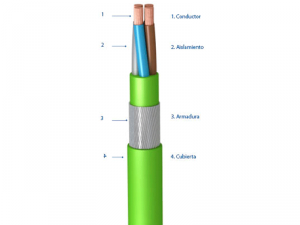
An electric cable consists of:
- Electric conductor: which channels the flow of electricity
- Insulation: it covers and contains the electric flow in the conductor.
- Auxiliary elements: that protect the cable and guarantee its longevity.
- Outer sheath: it covers all the mentioned materials protecting them from the outside.
Types of electric conductors
- Bare wire conductor: single wire in solid state, not flexible and without coating.
- Aluminum electrical conductors: in some cases, aluminum conductors are also used, despite the fact that this metal is 60% worse conductor than copper.
- Copper electrical conductors: the most commonly used material.
- Flexible copper wire conductor: it is a set of fine wires covered by an insulating material. They are flexible and malleable.
- Single-core cable: a cable with a single conductor.
- Multi-core cable: a cable that has several conductors.

TYPES OF INSULATION FOR ELECTRIC CABLES
The insulation consists of placing an insulating coating on the conductor to prevent current leakage. They are classified into two large groups: thermoplastic and thermoset.
1. Thermoplastic insulation
They are most common in the manufacture of electrical cables are:
- PVC:Polyvinyl chloride
- Z1: Polyolefins
- PE: Linear polyethylene
- PU: Polyurethane
2. Thermosetting insulation
The most common are:
- EPR: Ethylene Propylene
- XLPE: Crosslinked Polyethylene
- EVA: Ethyl Vinyl Acetate
- SI: Silicone
- PCP: Neoprene
- SBR: Natural Rubber
TYPES OF METAL PROTECTIONS FOR ELECTRICAL CABLES
In some cases, the cables may have metal shields.
- Screens: these are electrical metal protections applied to isolate the signals that pass through the interior of the cable from possible external interference.
- Armours: these are mechanical protections that protect the cable from possible external aggressions: animals, blows, etc.
NOMENCLATURE OF ELECTRICAL CABLES ACCORDING TO STANDARDS
Each cable has a standard designation. This designation is composed of a set of letters and numbers, each with a specific meaning. This designation refers to a series of product characteristics (materials, nominal tensions, etc.) that facilitate the selection of the most suitable cable for your needs, avoiding possible errors in the supply of one cable by another.
When a cable does not clearly indicate these data, it may be a defective cable, which does not comply with safety regulations or guarantee the cable’s life and proper operation.
Designation according to type of insulation
| Nomenclature | Electrical Cable Types |
|---|---|
| R | Crosslinked polyethylene (XLPE) |
| X | Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) |
| Z1 | Halogen-free thermoplastic polyolefin |
| Z | Halogen-free thermosetting elastomer |
| V | Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) |
| S | Halogen-free thermosetting silicone compound |
| D | Ethylene-propylene elastomer (EPR) |
Screen designation, interior lining, armature seat
| Nomenclature | Electrical Cable Types |
|---|---|
| C3 | Copper wire screen, helically arranged |
| C4 | Copper shield in the form of a braid, on the assembled insulated conductors. |
| V | Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) |
| Z1 | Halogen-free thermoplastic polyolefin |
If there is no screen, no inner lining and no armature seat, no letter is used.
Designation of the different types of armor
| Nomenclature | Electrical Cable Types |
|---|---|
| F | Steel strapping arranged in a helical pattern. |
| FA | Aluminium strapping arranged in a helical pattern |
| FA3 | Longitudinally corrugated aluminium strip |
| M | Steel wire crown |
| MA | Aluminium wire crown |
Designation of the outer sheath
| Nomenclature | Electrical Cable Types |
|---|---|
| V | Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) |
| Z1 | Halogen-free thermoplastic polyolefin |
| Z | Halogen-free thermosetting elastomer |
| N | Vulcanized chlorinated polymer |
Conductor’s designation
| Nomenclature | Electrical Cable Types |
|---|---|
| K | Flexible copper (class 5) for fixed installations |
| F | Flexible copper (class 5) for mobile services |
| D | Flexible for welding machine cables. When there are no letters on it, the conductor is made of solid copper, class 1 or 2. |
| AL | AL If the conductor is made of aluminium, (AL) is indicated. |
Rated voltage
| Rated | Voltage |
|---|---|
| 0,6/1 kV | Rated voltage 1,000V |
Explanation of the number of conductors
| Nomenclature | Electrical Cable Types |
|---|---|
| nGS | Number and cross-section of wires, in mm2 , with Yellow/Green conductor |
| nxS | Number and cross-section of conductors, in mm2 , without conductor Yellow/Green |
Cable design rules
The cable design rules are also referenced in the marking of each cable:
- UNE 21123
- IEC 60502
- UNE 21150
Additional data
| Nomenclature | Electrical Cable Types |
|---|---|
| CE | CE CE marking is compulsory for the marketing of the product in the European Community. This marking can be on the product or on the packaging. |
| Manufacture date | Date of manufacture (YYMMDD). The date of manufacture is usually placed for traceability purposes. Traceability makes it possible to know who, when and where has carried out each stage of the process and with which materials. |
You can review concepts through this video that we have prepared:

DIMENSIONING CRITERIA OF ELECRTICAL CONDUCTORS
There are two sizing criteria for copper conductors:
- In the AWG-American Wire Gauge, conductors are defined by specifying a number of wires and a diameter of each wire.
- In European sizing (mm2), the conductors are defined by specifying the maximum resistance of the conductor (Ω/km). Solid or flexible conductors are defined by specifying the minimum number of wires or the maximum diameter of the wires that form it. In addition, the actual geometrical sections are somewhat smaller than those indicated as nominal.
ELECTRICAL CABLE MEASUREMENTS
| CROSS-SECTION in mm2 | (AWG) | CURRENT CONSUMPTION | USED |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 mm2 | 4 | Very high | Central air conditioning and industrial equipment.. |
| 16 mm2 | 6 | High air | Conditioners, electric stoves and electric power connections. |
| 10 mm2 | 8 | Medium high | Refrigerators and dryers. |
| 6 mm2 | 10 | Medium | Microwave and blenders |
| 4 mm2 | 12 | Medium | Lighting |
| 2.5 mm2 | 14 | Under | Lamps |
| 1.5 mm2 | 16 | Very low | Thermostats, bells or security systems. |
Types of colours in electrical cables and their meaning
The colours of the electrical cables are governed by the International Electrical Commission Standard IEC 60446. For the identification of the conductors, the following colors are allowed: black, brown, red, orange, yellow, green, blue, violet, gray, white, pink and turquoise.
- Neutral conductor: blue. It is recommended not to use more blue conductors to avoid confusion.
- Phase conductor: black, grey or brown.
- Protective or earthing conductor: two colours, yellow and green. The use of yellow or green single-coloured cables is only permitted in places where, for safety reasons, there is no possibility of confusion with the earthing system.